Hello Friends, In this blog post(What Is Bluetooth Network) I am going to let you know about an interesting network that is known as the Bluetooth network.
In this blog post(What Is Bluetooth Network) we are going to cover the What type of network is Bluetooth? Is Bluetooth a wireless LAN? What are Bluetooth and its types? How do I set up a Bluetooth network?…
… What relation between Bluetooth and wireless networks? What is a Bluetooth network called? How do I connect to a Bluetooth network?|What Is Bluetooth Network|
Before going into detail let’s see a few Q&A about Bluetooth below:
What type of network is Bluetooth?
Bluetooth stands for wireless technology which allows you to share data and communicate with other devices in a short-distance area.
Bluetooth uses UHF radio waves for transferring data or communicating with another Bluetooth device.
The speed of data processing using Bluetooth is quite slow as compared to a wireless LAN.
Bluetooth builds a personal area network(PAN).
Is Bluetooth a wireless LAN?
Yes, up to a certain extent, we can say that Bluetooth is a wireless LAN.
Bluetooth is a wireless technology to communicate with other devices in a very short range and is used in sharing data.
The technology is based on Ad-hoc technology and is also known as Ad-hoc pico nets.
Bluetooth can be considered as a wireless LAN with a very limited or short coverage area.
What are Bluetooth and its types?
Bluetooth is a wireless technology to shares data between two or more devices over the air in a wide range of areas.
The distance between the two devices is very short from the fixed, and mobile devices and building the personal area network.
In 1994, The L.M Ericsson company became interested in connecting its Mobile phones to other devices(e.g. PDAs) without cables.
Four other companies(IBM, Intel, Nokia, and Toshiba), formed a SIG(special interest group, I,e consortium) to develop a wireless standard for…
… interconnecting computing, communication devices, and accessories using short-range, low-power, inexpensive wireless radios.
The project was named Bluetooth, after Harald Blaatand(Bluetooth)II(940-981), a Viking king who unified(i,e, conquered) Denmark and Norway, also without cables.
Although the original idea was just to get rid of the cables between devices, it soon began to expand in scope and encroach on the area of wireless LANs.
While this move makes the standard more useful, it also creates some competition for mindshare with 802.11.
To make matters worse, the two systems also interfere with each other electrically.
It is also worth noting that Hewlett-Packard introduced an infrared network for connecting computer peripherals without wires some years ago, but it never really caught on in a bit way.
The main goal of Bluetooth is to develop a single single-chip, low-cost, radio-based wireless network technology.
At the same time the Bluetooth development started, a study group within the IEEE 802.11 wireless personal area network(WPAN) discussed the following five criteria.
Distinct Identity:
Originally the study group did not want to establish a second 802.11 standard.
Compatibility:
Compatibility with IEEE 802 standard.
Market Potential:
How many applications, devices, vendors, and customers are available for a certain technology?
Technical Feasibility:
Prototypes are necessary for further discussion, so the study group would not rely on paperwork
Economic Feasibility:
Everything developed within this group should be cheaper than other solutions and allow for high-volume production.
Bluetooth fulfills these criteria so the WPAN group cooperated with the Bluetooth consortium.
To understand the networking of Bluetooth devices a quick introduction to its key features is necessary.
The basic unit of Bluetooth is Piconet, which consists of a master node and up to seven active slave nodes within a distance of 10 meters.
Multiple piconets can exist in the same(large) room and can even be connected via a bridge node as shown in Fig 1.
An interconnected collection of a piconet is called a ScatterNet.
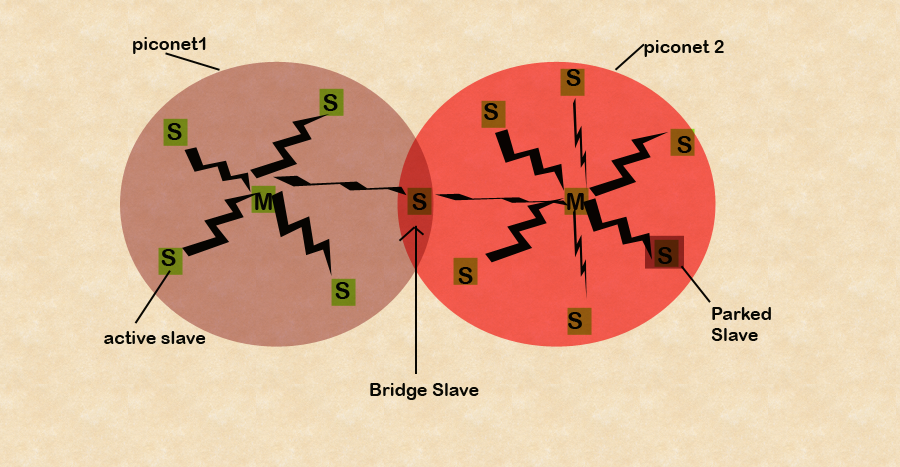
There can be up to 255 parked nodes in the net for the seven active slave nodes in a piconet.
These are devices that the master has switched to a low-power state to reduce the drain on their batteries.
In the Parkes state, a device can not do anything except respond to an activation or beacon signal from the master.
There are also two intermediate power states, hold and sniff.
The reason for the master/slave design is that the designers intended to facilitate the implementation of complete Bluetooth chips for under $5.
The consequence of this decision is that the slaves are fairly dumb, basically just doing whatever the master tells them to do.
Thus, a piconet is a centralized TDM system, with the master controlling the clock and determining which device gets to communicate in which time slot.
All communication is between the master and a slave; direct slave-slave communication is not possible.
Applications:
802.11 does not specify whether users should use their notebook computers for reading emails, surfing the web, or something else.
In contrast, the Bluetooth V1.1 specification names 13 specific applications to be supported and provides different protocol stacks for each one.
Unfortunately, this approach leads to a very large amount of complexity, which we will omit here. The 13 applications, which are called profiles, are listed in below Fig 2
| Name | Description |
| Generic Access | Procedure for link management |
| Service Discovery | Protocol for discovering offered services |
| Serial Port | Replacement for serial port cable |
| Generic Object Exchange | Defines client-server relationship for object movement |
| LAN Access | protocol between a mobile computer and a fixed LAN |
| Dial-Up Networking | Allows a notebook Computer to call via a mobile phone |
| FAX | Allows a mobile fax machine to talk to a mobile phone |
| Cordless Telephony | connects a handset and its local base station |
| Intercom | Digital walkie-talkie |
| Headset | Allows hands-free voice communication |
| Object Push | provides a way to exchange simple objects |
| File Transfer | Provides a more general file transfer facility |
| Synchronization | Permits a PDA to synchronize with another computer |
Fig 2 Bluetooth Profiles
The first generic access profile is not an application, but rather the basis upon which the real applications are built.
Its main job is to provide a way to establish and maintain secure links between the master and slaves.
Also relatively generic are the services other devices have to offer.
These two profiles are necessary for Second Bluetooth devices. The remaining one is optional.
The serial port profile is a transport protocol that most of the remaining profiles use.
It emulates a serial life and is useful for legacy applications.
The generic object exchange profile defines a client-server relationship for moving data around.
The next three profiles are for networking. The LAN access profile allows a Bluetooth device to connect to a fixed network.
this profile is a direct competitor to 802.11.
The dial-up network protocol is used to allow a notebook computer to connect to a mobile phone containing a built-in modem without wires.
The fax profile is similar to dial-up networking except that it allows wireless fax machines to send the receive faxes using a mobile phone without a wire between the two.
The next three profiles cordless telephony, intercom, and headset profiles, are for telephony.
The remaining three profiles are for actually exchanging objects between two wireless devices.
These could be business cards, pictures, or data files, The synchronization profile, in particular, is intended for loading into a PDA or notebook computer when it leaves home and collecting data from it when it returns|Bluetooth Network|
You can also go through a few more amazing blog links below related to computer networks:
Need Of Network Layer In Computer Network…
What Is Wireless LAN In Computer Networks…
What Is Bluetooth Network…
FDDI Network In Hindi…
What is a Token Ring(802.5) In a Computer network…
What is a token bus in the computer network…
What is Ethernet In Hindi…
Compare Ethernet802.3, Token Bus802.4…
CSMA(Carrier Sense Multiple Access In Hindi) In Hindi…
What is the design issue of the network layer…
Conclusion:
Using this blog post(What Is Bluetooth Network) we have gone through What type of network is Bluetooth, whether Is Bluetooth a wireless LAN, What is Bluetooth and its types, How do I set up a Bluetooth network, and What relation is between Bluetooth and wireless networks? Bluetooth is a younger wireless technology where two devices can transfer data over the air without any wire or any physical touch. Bluetooth uses radio waves to transfer data from one device to another.
In the case of any queries, you can write to us at a5theorys@gmail.com we will get back to you ASAP.
Hope! you would have enjoyed this post about What Is Bluetooth Networks.
Please feel free to give your important feedback in the comment section below|What Is Bluetooth Network|
Have a great time! Sayonara!

Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.